Trochanteric bursitis
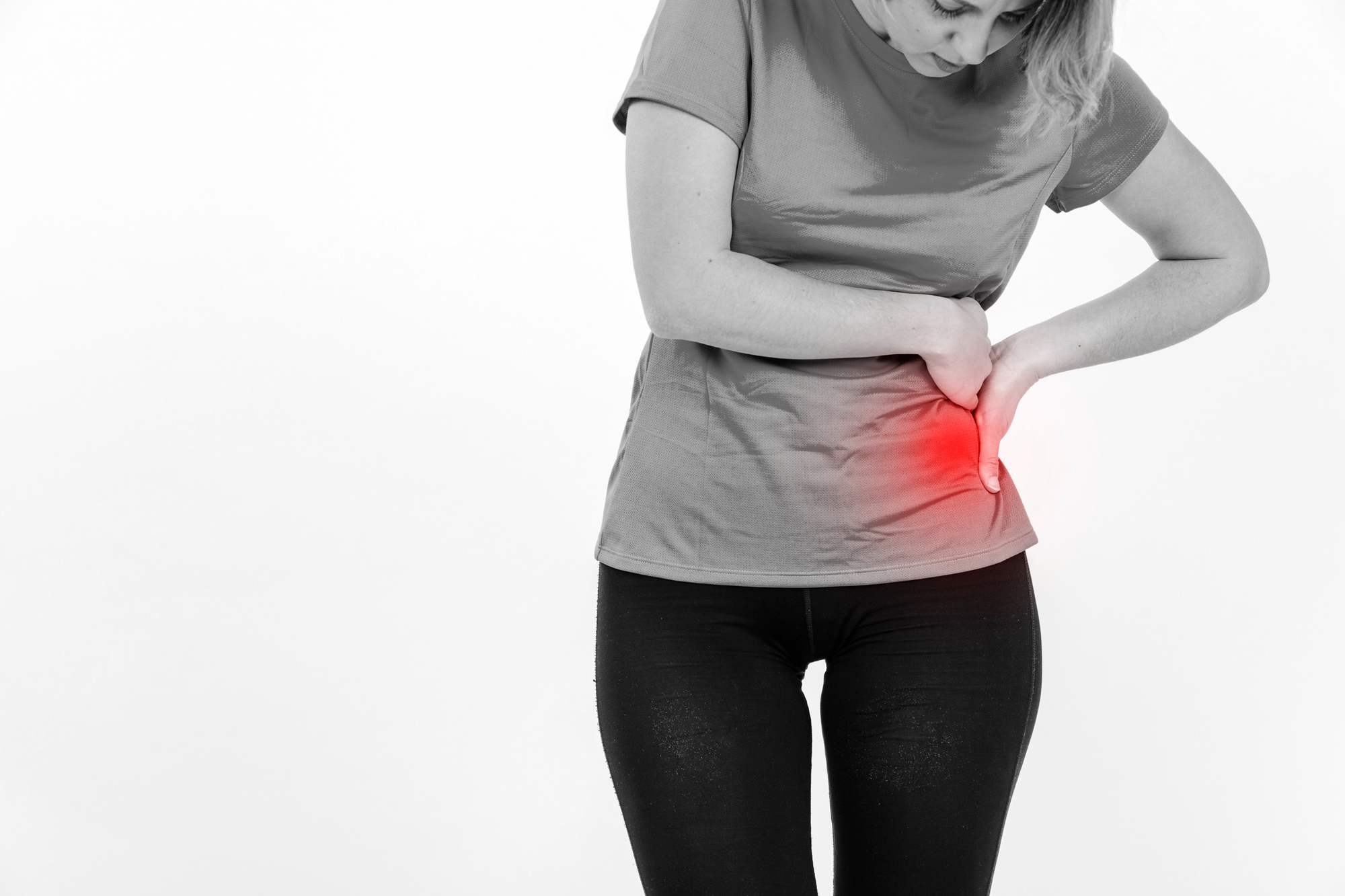
What is trochanter bursitis?
Trochanteric bursitis is an inflammation of the bursa, a small fluid-filled sac that acts to reduce friction between tendons, muscles and bones in the hip. The greater trochanter, which is a bony prominence on the thigh bone (femur), is the site of the bursa involved in trochanteric bursitis. When this bursa becomes inflamed, it can lead to pain and discomfort in the hip, which can affect one’s ability to walk and perform daily activities.
Trochanteric bursitis is a common cause of hip pain, especially in middle-aged and older individuals, as well as in athletes who subject their hips to repetitive strain. Understanding its symptoms, causes and treatments is crucial to managing and relieving this painful condition.
Causes and risk factors
Causes
Trochanteric bursitis can occur for several different reasons. Some of the most common causes include:
Overuse: Repeated movements or prolonged stress on the hip, such as running, cycling or standing, can irritate the bursa and lead to inflammation.
Injuries: A direct injury, such as a fall or a blow to the hip, can damage the bursa and cause inflammation.
Improper gait: Gait disturbances due to leg length discrepancy, incorrect posture or foot problems can increase stress on the hip and lead to bursitis.
Arthritis: Inflammatory joint diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis can increase the risk of developing trochanteric bursitis.
Surgery: Hip surgery or other procedures can sometimes lead to irritation of the bursa and subsequent inflammation.
Also read our article on: Trochanteric bursitis treatment
Risk factors
Several factors can increase the risk of developing trochanteric bursitis:
Age: The risk of trochanteric bursitis increases with age, especially after the age of 40.
Gender: Women are more likely to suffer from trochanteric bursitis than men, which may be due to wider pelvis and different biomechanics of the hip.
Occupation and activity: Occupations and activities that involve repetitive movements or prolonged stress on the hip increase the risk of bursitis.
Overweight: Being overweight can put extra strain on the hip, which can contribute to the development of bursitis.
Exercise habits: Sudden increases in exercise intensity or insufficient warm-up before physical activity can increase the risk of injury and inflammation of the hip.
Symptoms and diagnosis
Symptom
The most common symptoms of trochanter bursitis include:
Pain on the outside of the hip: The pain is usually localized over the greater trochanter and may radiate down the outside of the thigh. The pain can be sharp and intense, especially with movement, and is often worse with physical activity or when lying on the affected side.
Tenderness: The area over the trochanter may be tender to the touch, making it uncomfortable to sit or lie on the affected side.
Swelling and redness: In some cases, the area around the bursa may become swollen and red, which is a sign of inflammation.
Pain on movement: Activities such as walking, running or lying on the affected side can make the pain worse. Climbing stairs, sitting too long or standing up can also increase pain.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of trochanteric bursitis is made by a combination of the patient’s medical history, physical examination and, if necessary, imaging. The most common methods for diagnosing trochanteric bursitis include:
Medical history: The doctor will ask about your symptoms, when they started and what seems to aggravate or relieve them.
Physical examination: The doctor will examine the hip and the affected area to assess soreness, swelling and range of motion.
Imaging diagnostics: To rule out other possible causes of hip pain, such as stress fractures or arthritis, the doctor may order an X-ray, ultrasound or MRI.
Treatment options
Medical treatments
The treatment of trochanteric bursitis aims to reduce pain and inflammation, as well as to prevent recurrence. Common medical treatment options include:
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Drugs such as ibuprofen or naproxen can be used to reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
Cortisone injections: Injections of cortisone directly into the bursa can provide rapid and effective relief of inflammation and pain. The effect of cortisone injections can be long-lasting, but in some cases multiple injections may be needed over time.
Physiotherapy: A physiotherapist can design an exercise programme to strengthen and stabilize the hip area, which can help reduce pain and improve function. This may include stretching, strengthening exercises and techniques to improve walking and posture.
Surgery: In rare cases, when other treatments have not been effective, surgery may be necessary to remove the bursa. However, this is a last resort and is only used when all other treatment methods have failed.
Home care and self-care
In addition to medical treatments, there are several self-care measures that can help relieve the symptoms of trochanteric bursitis:
Rest: Avoiding activities that aggravate the pain can help reduce inflammation. It is important to give the hip time to recover by reducing or avoiding repetitive movements that can aggravate the condition.
Ice treatment: Applying ice to the affected area for 15-20 minutes several times a day can help reduce swelling and pain. This can be particularly effective immediately after physical activity or when the pain is at its worst.
Stretching and strengthening exercises: Specific exercises aimed at strengthening the hip and gluteal muscles and improving flexibility can be helpful. A physiotherapist can provide guidance on appropriate exercises and stretching techniques.
Prevention
Taking preventive measures can reduce the risk of developing trochanteric bursitis or prevent recurrence:
Avoid overloading: Increase the intensity of physical activities gradually to avoid overloading the hip. This means avoiding too large increases in exercise intensity or duration.
Use the right equipment: Wear shoes that provide sufficient support and cushioning to reduce stress on the hip. Shoes with good shock absorption can help distribute weight evenly and reduce stress on the hip joint.
Correcting gait problems: If there is leg length discrepancy or other gait problems, orthopedic inserts or other corrective measures may be needed. A physiotherapist can help identify and correct walking problems that may contribute to bursitis.
Warm up and stretch: Regular stretching and warming up before physical activity can help prevent injury and inflammation. It is important to include stretching of the hip muscles and other related muscle groups in your daily routine.
When should you seek medical help?
Indications for medical assistance
If the pain does not improve with self-care measures, if it gets worse, or if other symptoms such as fever or difficulty moving the hip occur, medical help should be sought. It is important to get a proper diagnosis and treatment to prevent the condition from getting worse.
Forecast and recovery
The prognosis for trochanteric bursitis is generally good with proper treatment. Most people recover fully and can return to their normal activities within a few weeks to months, depending on the severity of their condition. Long-term management and prevention are important to reduce the risk of recurrence.
How can we help you with trochanter bursitis?
Understanding the causes and symptoms is the first step towards finding effective relief for your condition. At the FasciaClinics, we take a holistic approach to treating trochanteric bursitis. Our team of therapists use fascia therapy to relieve tension and pain in our body. The fascia is the network of connective tissue that binds and permeates everything in our body. All cells, tissues (even bone tissue), muscles and organs contain fascia.
Fascia treatment focuses on releasing tension and adhesions in the fascia and increasing its flow. Reduced pressure and increased circulation allow cell membranes to more easily absorb nutrients and release waste products. Fascia treatment can thus promote the body’s own healing. The treatment provides a pleasant relaxation and does not hurt. It gets the whole body flowing and helps you balance your posture so that the body is evenly loaded.
During a visit, we analyze the whole body to see where compensations and imbalances are and how they have spread. If there is an imbalance in the body, there is a risk that it will spread and affect other structures such as muscles and joints. That’s why it’s very important to seek help quickly as soon as you notice any symptoms.
Fascia treatment for trochanteric bursitis involves balancing the body by adjusting the pelvis to even out the load on the trochanters and reduce pressure on the bursa. We also work on softening the fascia in the muscles, joints and ligaments around the hips and seat. A more even load will mean that muscles and other structures are not exposed to as much wear and tear and thus reduce the risk of injury.
Contact us today to get the help you need and start your journey towards a pain-free and active life. Our team of fascia therapists is here to support you through every step of your recovery and help you achieve the best possible results. We aim to give you the care and attention you deserve, so you can return to your daily activities without pain and discomfort.
 Search
Search