What is an inflammation?

Inflammation is the body’s response to an injury, irritation or infection. Acute inflammation occurs when there is an injury or infection and involves the activation of the body’s immune system to create healing in the injured or infected tissue. Normally, the inflammation clears up within a week and the injured tissue heals, but sometimes the inflammation may linger. The cause of the injury, tear or infection may still be there, or something may be missing that causes the healing process to fail and not complete. The inflammation may then become chronic. Being chronic means that it is long-lasting but not necessarily lifelong.
Inflammation or infection?
It is essential to distinguish between inflammation and infection as these tend to be confused. The concepts are related but they describe two completely different conditions. An infection is an attack by an infectious agent (e.g. virus, bacterium, fungus) that has entered the body. Inflammation is the body’s response to an infection or injury. In principle, an infection always leads to inflammation, which occurs because the immune system is activated to defend and heal the area where the infection has occurred. However, inflammation can occur whether or not there is an infection. Injuries, such as fractures, blisters or overexertion due to repetitive movements, can cause inflammation as tearing, fatigue and micro-injuries occur in the tissue, without there being an infection.
How does an inflammation occur?
When inflammation occurs in an area, the immune system starts releasing signaling substances to call in more defense cells, in the form of different types of white blood cells. The white blood cells make their way to the injured area, increasing the blood supply and dilating the vessels so that they start leaking substances into the injured area. This is done mainly to allow the white blood cells to come out of the blood and work in the injured area.
The blood flow to the area increases, causing redness if it occurs in the skin. With the increased circulation and activity, redness, swelling, heat and pain occur due to increased pressure on nerve receptors and also substances that irritate pain receptors. The swelling occurs because the vessels are leaking and more white blood cells must quickly arrive at the injured area. Now an acute inflammation has been created. The body acts like this to try to close off the injured area and stop the flow, so that, for example, bacteria do not spread to a larger area. Inflammation is thus in itself an important and natural healing process that the body has.
Chronic inflammation
When the body is unable to heal the damaged area, the inflammation turns into chronic, i.e. long-lasting. What happens when the inflammation becomes chronic? The body’s immune system continues to work and then you will mainly experience continued pain. Chronic inflammation is caused by too much strain in the tissue that the body does not have time to handle, so-called oxidative stress. For example, other inflammations can occur in the body at the same time.
Chronic inflammation is thus a precursor to many diseases. The pathway between chronic inflammation and other diseases can be understood by oxidative stress and there are more podcasts [1] and articles on the Fascia Guide to share this information. The article “Oxidative stress – Is your body rusting too?” on the Fascia Guide, discusses the relationship between chronic inflammation and other diseases in more detail.
Symptoms of inflammation
Inflammation causes pain, where the pain comes from the free nerve endings being irritated, partly chemically by what the white blood cells release, but also by the pressure caused by increased fluid accumulation. As a result, there is swelling, pain, heat, redness and dysfunction that can affect mobility as a certain part of the body cannot be used in the same way as before.
Causes and Symptoms of General Inflammation in the Body
The symptoms of inflammation are pain, swelling, heat, redness and loss of function. In general, if the inflammation affects most of the body, the whole system, you may have a fever. It is usually referred to in terms of ‘low-grade fever’ and ‘high fever’, where the former is due to localized inflammation, while high fever affects the whole body. It is the increased activity and metabolism that raises the temperature, heat locally or fever throughout the system. Below are the symptoms of inflammation in different parts of the body.
Causes of Inflammation of the Back
In several studies conducted by Siegfried Mense and Hoheisel in 2011-2019, they concluded that all back pain is caused by inflammation in the back. The inflammation creates a tearing of the free nerve endings found in the fascia of the back muscles, most commonly in the lumbar or lower thoracic spine. Flow is impaired and the fascia becomes denser with increased pressure on pain receptors, as well as increased numbers of pain receptors signaling more pain.
Back pain can be caused by an acute injury, strain, etc., but also by prolonged incorrect loading with a poor ergonomic working position or heavy lifting. Back pain can usually be traced back to how we live, that is, our lifestyle. A lot of sitting leads to back pain, while exercise and movement are good for the back. All movement benefits the flow and reduces inflammation. When the problems with back pain start to appear, the pain in turn leads to most people trying to spare the area that hurts, by moving less and above all compensating and not moving in balance. This in turn will cause the flow in the fascia to be imbalanced and the body parts that are held still will stiffen even more as the flow in the fascia becomes more viscous and the network of collagen fibers becomes denser.
Symptoms of Inflammation of the Back
An inflammation leads to an increasing pressure on pain receptors, as well as an increase in the number of pain receptors that signal more pain. Severe pain when moving but also when sitting or lying down. Can cause sleep problems and difficulties with everyday tasks. Mobility in the back is also markedly impaired, both due to pain and compression.
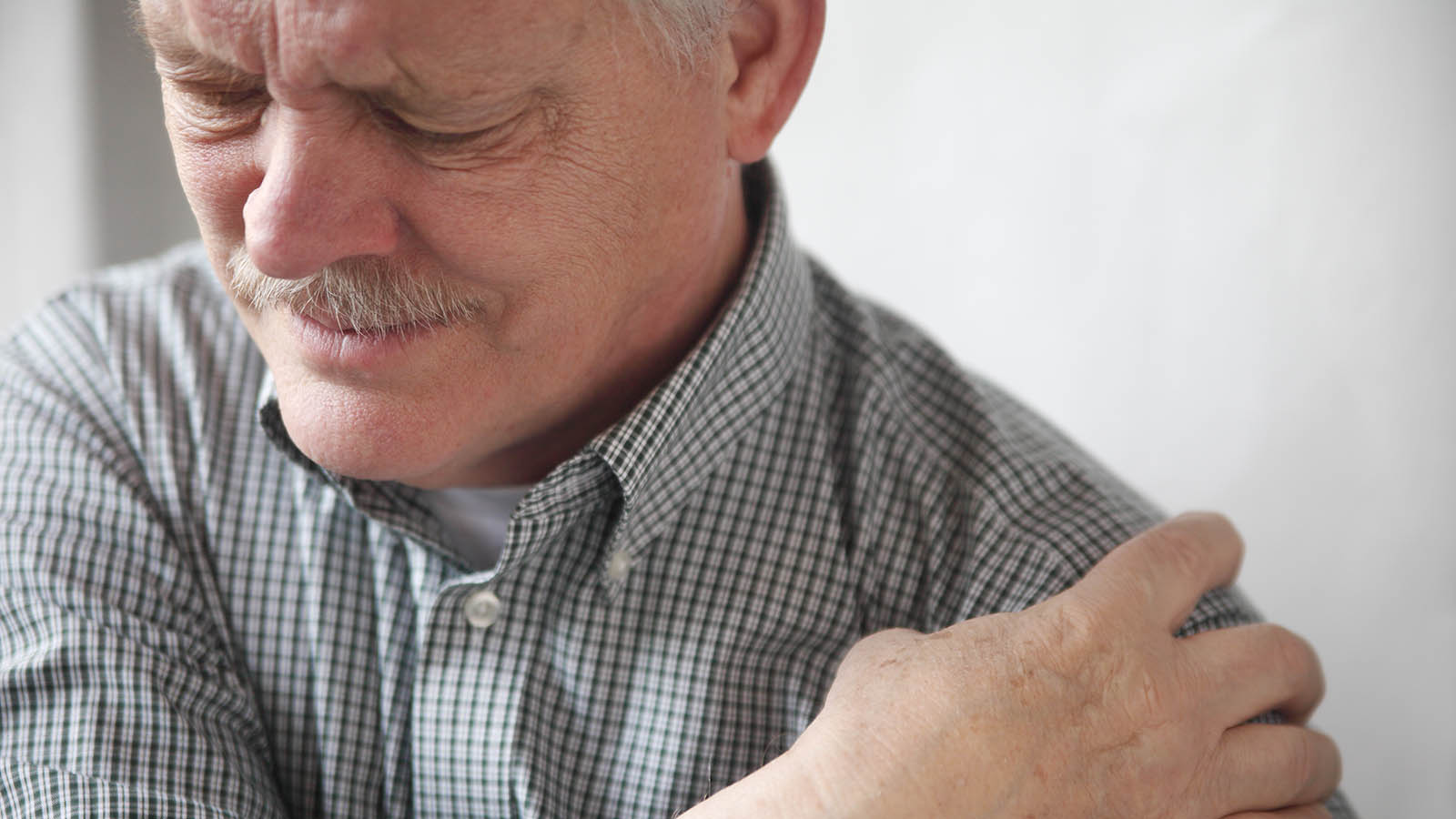
Causes of Inflammation of the Shoulder
A shoulder can also become inflamed, which can happen when the area becomes overstressed, which in turn can be due to, for example, overloading the shoulder with repetitive movements. We may be carrying a lot of weight and repeatedly for a long time, and may be working in a bad position for the shoulder. There may also be an injury to the shoulder that causes the body to create inflammation, such as a strain or landing on the shoulder during a fall. When falling on the shoulder, the shoulder joint is easily dislocated as it has a shallow socket. A dislocation then gives rise to inflammation. Depending on the healing process, the inflammation can be short- or long-term. If it is long-lasting, a chronic inflammation, it can be the precursor to frozen shoulder.
Symptoms of Inflammation of the Shoulder
An inflamed shoulder causes pain and discomfort. Mobility is impaired, making it difficult to move the arm behind the back. Muscle strength can also be affected due to nerve damage and you lose strength as your arm moves outwards.
Causes of Inflammation of the Knee
Inflammation of the knee usually arises from twisting, oblique loading, repeated jumps but above all incorrect posture or rotated oblique pelvis. Good posture and maintaining balance is therefore important so that both sides of the spine and the pelvis are equally loaded. Another example of inflammation in the knee can be due to missteps in running training, as there is then an impact between the foot and the ground when landing and when the repeated load becomes too great, micro damage can occur in fascia structures around the knee and an inflammation is created in the injured area.
Symptoms of Inflammation of the Knee
Inflammation of the knee causes pain on exertion, which can make it difficult to move. There may also be aching pain at rest. You may feel warmth and swelling with possible fluid filling in the knee.
Causes of Inflammation in the Chest
If you have a compressed chest and poor mobility, due to a compressed posture combined with infrequent deep breathing, then there is poor movement in the lungs and chest. This can lead to inflammation of the muscles and fascia around the chest. The inflammation itself also causes poor mobility so it becomes a vicious circle. This also affects breathing, diaphragm, lymph flow and ultimately the immune system and overall well-being.
Symptoms of Inflammation in the Chest
Symptoms of inflammation in the chest muscles and around the ribs can be difficulty breathing, a perceived feeling that it is difficult to take deep breaths, you exhale and take many small breaths instead of fewer and deeper. Inflammation in the chest muscles, rib muscles and fascia can cause a compressed posture that makes it harder to breathe so that you rarely breathe deeply, there is poor movement in the lungs and chest. Poor posture gives poor mobility, which affects breathing, diaphragm, lymph flow and then also the immune system and general well-being.
Muscle inflammation
Inflammation in a muscle can result from overuse, repetitive motion or if the muscle has been injured, for example by a blow or stretch. An injury or tear can affect single or many muscle fibers, but it is more common for the fascia around muscle bundles or the stronger fascia around an entire muscle or muscle group to be damaged, with collagen fibers being torn.
When there is inflammation in the muscle, the person experiences pain which can also spread to other parts of the body. The mobility of the inflamed part of the body will be impaired and this will also affect other parts of the body.
However, the inflammation is not in the muscle fibers or muscle cells, but in the fascia itself, inside and around the muscle. All nerve endings and nerve receptors are located in the fascia of the muscle and are affected by and signal pain during inflammation. This in turn creates a vicious circle as the brain registers this and contributes even more teasing. One way to get rid of the inflammation is movement as well as treatment to stimulate flow and provide good nutrition, to reduce oxidative stress. Therefore, it can be beneficial to provide the body with anti-inflammatory preparations such as turmeric, magnesium and vitamin C.
There is an additional way to overcome this problem, through the injection or ointment of cortisone or other anti-inflammatory drugs into the injured area. However, the problem with this is that cortisone relieves the pain but does not remove the cause of the inflammation in the first place. Repeated cortisone treatment in excessive doses also has other negative side effects.
Inflammation is created by the body to heal something, but when the body is unable to heal it itself, that’s when you have problems. The reason why the body fails to heal it itself is probably because we have exposed ourselves to too much strain or oxidative stress. The best solution is to treat the inflammation by relaxing the body, not stressing, maintaining good posture and balance, eating a healthy diet without processed foods and additives, reducing sugar consumption, eating the right nutrients and building blocks for the body to feel good, and providing the body with certain antioxidants, minerals and vitamins.
Inflammation of joints
If there is inflammation in a joint, the ability to move in the area of inflammation is impaired. The causes of an inflamed joint can be very many, it can be due to rheumatic problems or for example osteoarthritis. But usually it is something milder, such as an overexertion of the joint, a sprain or a misstep, and therefore need not be so serious. It is common to get an inflammation of the wrist or inflamed Achilles tendon.
If there is inflammation in a joint, it is important to ensure that the load on the joint is balanced. Other possible chronic inflammations in the body should be taken care of so that they heal as well as possible. They can be caused by stress, lack of sleep, nutritional deficiencies, unhealthy diets with processed foods, high sugar, depleted gut flora, coffee, alcohol, smoking and other toxins, and more. All of this puts a huge strain and creates oxidative stress, which means too many free radicals trying to bind to electrons and thus consuming the large amounts of antioxidants that would be needed to heal a joint inflammation, for example. With a large consumption of antioxidants in all types of stress and strain we expose the body to, a deficiency soon arises if they are not supplied through the body’s own production, diet or supplements. Therefore, it is beneficial to take supplements so that the body can cope with the damaged area.
 Search
Search