Common injuries in athletics & gymnastics – Prevention and treatment
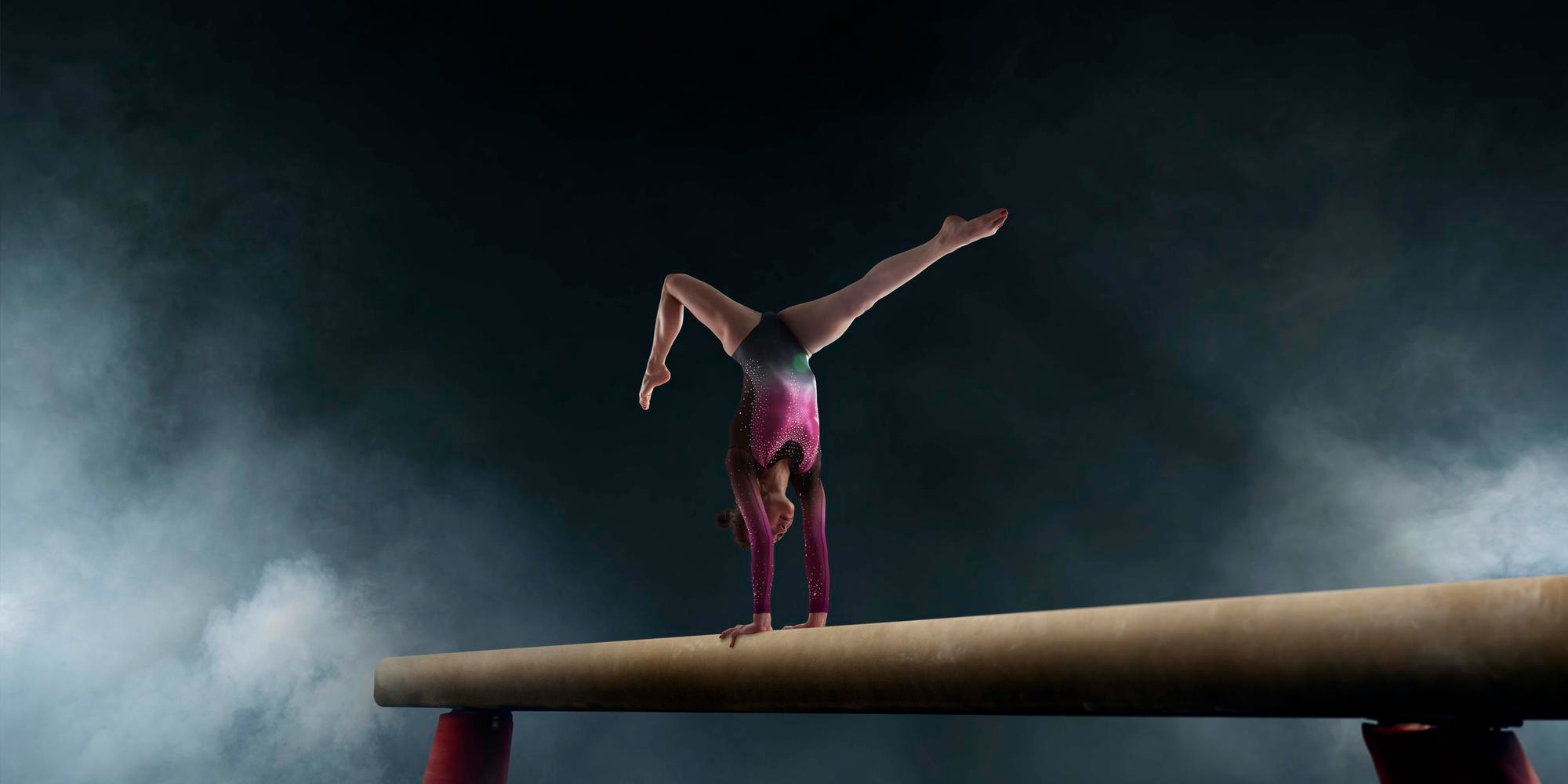

Athletics and gymnastics are sports that require explosive strength, agility and precision. Athletes strain their bodies through repeated jumps, landings, sprints and powerful movements, increasing the risk of injury. To avoid long rehabilitation periods and reduce the risk of injury, it is important to understand the most common injuries, their causes and how to prevent them.
In this guide, we look at the most common injuries in athletics and gymnastics, their causes, and how they can be prevented and treated. We also explain how Fascia Clinics can help you optimize recovery and prevent future injuries through fascia treatment and personalised rehabilitation.
Common types of injuries in athletics & gymnastics
The most frequent injuries in athletics and gymnastics occur due to high loads on muscles, tendons and joints. Here are some of the most common injuries:
Knee injuries (meniscus injuries and patellar tendinitis)
Meniscus injuries: Occurs when twisting sharply or landing quickly after jumping. A damaged meniscus can cause pain, swelling and instability in the knee.
Patellar tendinitis (jumper’s knee): An overuse injury affecting the patellar tendon. Common symptoms include pain under the kneecap, especially when jumping and running.
Shoulder injuries (overuse and rotator cuff injuries)
Overloading the shoulders: Gymnasts and athletes in throwing events subject their shoulders to repetitive movements, which can lead to inflammation and pain.
Rotator cuff injuries: Damage to the muscles and tendons that stabilize the shoulder joint. Can cause pain and limited mobility.
Stress fractures
Occurs in the legs and feet due to prolonged overload and repetitive impact.
Common in long-distance runners and jumpers. Symptoms include pain that worsens with activity and reduces at rest.
Ankle injuries and sprains
Ligament damage in the ankle: Common during jumps and quick turns. Can cause pain, swelling and instability.
Sprains: Involves stretching or tearing the ligaments in the ankle, which can affect balance and mobility.
Muscle tears (hamstrings and calf muscles)
Hamstring strains: Often affects sprinters and jumpers during explosive movements. Symptoms include sudden pain and reduced strength in the back of the thigh.
calf muscle injuries: Common in powerful push-offs, e.g. sprinting and jumping. May cause stiffness and difficulty in extending the foot.
Causes and risk factors of injury in athletics & gymnastics
Injuries in these sports are often caused by a combination of high impact, repetitive movements and biomechanical imbalances.
Common causes of injury:
Overtraining – Lack of rest and recovery can lead to muscle and joint fatigue.
Repetitive movements – Repeated jumps, throws and sprints increase the risk of overuse injuries.
Lack of proper technique – Incorrect landings or poor biomechanics can lead to injury.
Too little warm-up – If muscles and joints are not warmed up, the risk of strains and tears increases.
Weak stabilizing muscles – Imbalances between different muscle groups can lead to misuse and injury.
Injury prevention in athletics & gymnastics
Prevention is the key to staying injury-free and performing at your best.
1. proper warm-up and stretching
Dynamic warm-up exercises increase blood flow and prepare the body for movement.
Stretching after exercise helps to maintain mobility and reduce muscle stiffness.
2. Strength and stability training
Build strength in your knees, hips and shoulders to reduce the risk of overuse injuries.
Core training improves stability and reduces stress on the spine and joints.
3. Technical training
Learn proper landing and running techniques to reduce stress on joints and muscles.
Work with a trainer or physiotherapist to identify and correct biomechanical imbalances.
4. Gradual increase in exercise intensity
Avoid increasing the training load too quickly, especially for jumps and explosive movements.
Listen to your body and rest if you feel pain or stiffness.
Treatment of common injuries in athletics & gymnastics
When injuries occur, it is important to take the right steps to speed up recovery.
Acute treatment (RICE method)
R (Rest) – Rest the injured body part.
I (Ice) – Apply cold to reduce swelling.
C (Compression) – Use bandages to limit swelling.
E (Elevation) – Hold the injured body part high to reduce blood flow.
Rehabilitation and return to training and competition
Physiotherapy and fascia treatment help speed up recovery and improve mobility.
Strength training and stability exercises to reduce the risk of recurrent injury.
Gradual return to low impact exercise before full intensity.
How our specialist team at Fascia Clinics can help you
At Fascia Clinics, we offer specialized treatment and rehabilitation for athletes and gymnasts. Our fascia treatments and individualized training programs can help you to:
Reduce pain and stiffness by optimizing fascia and muscle tissue.
Accelerate recovery through treatments that improve circulation and reduce inflammation.
Preventing future injuries by identifying and correcting biomechanical imbalances
Whether you’re an athlete or a recreational user, we can help you stay injury-free and optimize your performance. Visit fasciaklinikerna fasciaklinikerna.se to book a consultation and get a customized treatment plan!
 Search
Search